원인 불명의 열(원인 불명 열/불명 열), Fever of unknown origin(FUO)
원인 불명의 열의 정의

사진 8-6. 열이 나는지 알기 위해 체온을 잰다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
- 열이 소아들에게 8일 동안이나 그 이상, 성인들에게서 3주 동안 또는 그 이상 계속 나지만 열이 나게 하는 확실한 원인을 진찰 소견과 처음 한 임상검사 등으로 찾지 못할 때의 열을 원인 불명 열(원인 불명의 열 또는 불명 열)이라고 정의하기도 하고,
- 14일 동안에 적어도 체온이 38.3°C(101°F)이거나 그 이상의 열이 적어도 4시간동안 지속되고, 그런 열이 적어도 4번이나 그 이상 나면 원인 불명의 열이라고 정의하기도 한다.
소스; Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.245 - 또 그 외 달리 정의하기도 한다.
원인 불명의 열의 원인
- 열이 성인들에게서 3주나 그 이상, 소아들에게 8일이나 그 이상 계속 나지만 열을 나게 하는 원인을 열심히 찾아도 원인을 찾지 못할 때의 열을 원인 불명의 열이라 진단한다.
- 병원에서 열이 나는 원인을 7일간 찾았는데도 원인을 찾지 못할 때의 열을 원인 불명의 열이라 진단하기도 하고,
- 병원 밖에서 3주 이상 나는 열의 원인을 찾아도 열나는 원인을 찾지 못할 때 원인 불명의 열이라 한다.
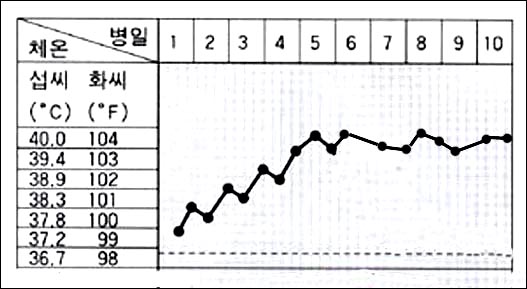
그림 37. 처음 한 진찰 소견과 임상검사로 열나는 원인을 확실히 찾을 수 없이 열이 8일 동안 또는 그 이상 계속 나거나(소아의 경우), 3주 동안이나 그 이상 열이 계속 나면(성인의 경우), 원인 불명 열이라고 정의할 수 있다 제21권 소아청소년 가정 ․학교 간호 참조문헌 및 출처-11.
원인 불명의 열의 진단
- 열이 8일 내지 2주 이상 계속 나고 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 현재 병력, 증상, 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하고 적절한 임상검사를 해도 열이 나는 원인을 확실히 찾지 못할 때는 원인 불명 열이라고 한다. 이와 같은 원인 불명 열을 여러 가지로 정의한다.
- 결핵, 그 외 각 종의 감염병,
- 암,
- 백혈병,
- 요로 감염 등으로 열이 날 수 있다. 그런 병이 있을 때 왜 열이 나는지 알아보기 위해서 적절한 검진, 임상검사 등을 반복해도 처음 얼마 동안은 확실히 진단을 붙이지 못할 수 있다.
- 애완용 거북이나 뱀에서 살모넬라균에 감염되어 살모넬라균 감염병에 걸리거나,
- 잘 관리되지 않은 참외나 수박 등을 먹은 후 살모넬라균에 감염되어 살모넬라균 감염병에 걸릴 수 있다. 이런 감염병에 걸렸을 때 처음 며칠 동안 진단을 확실히 붙이지 못해 원인 불명 열로 진단을 내리기도 한다.
- 어떤 특정 지역이나 나라에 여행 갔을 때 그 지역에서만 유행되는 말라리아,
- 록키 마운틴 스파티드 열(Rocky mountain spotted fever)
- Q 열 등 특정지역 특정 감염병에 걸려 열이 8일 이상 계속 날 수 있다. 이런 병에 걸렸는지 몰라 처음 얼마 동안 진단을 붙이지 못해 원인 불명 열이 난다고 진단 내리기도 한다.
- 생우유를 먹은 후 브루셀라 병(Brucellosis disease)에 걸려 열이 8일 이상 계속 날 수 있다.
- 익히지 않은 음식물을 먹은 후 유충 장기 이행증, 장질부사 등 감염병에 걸려 8일 이상 계속 열이 날 수 있다.
- 원인 불명의 열의 20%는 열이 나게 한 원인을 찾으려고 암만 애 써도 열이 나는 원인이 확실히 규명되지 않은 채로 자연히 열이 없어질 수 있다.
소아청소년들에게 있는 원인 불명 열의 80%는 다음과 같은 감염병이나 병으로 생긴다.
① 바이러스(성) 감염병
② 부루셀라 병
③ 장질부사
④ 야토병(Tularemia)
⑤ 충수염과 그로 인한 농양
⑥ 골수염
⑦ 연소성 류마토이드 관절염
⑧ 염증성 장염
⑨ 악성 종양
⑩ 완전히 치료되지 않은 뇌막염
⑪ 가와사키 병
⑫ 묘조병(묘소병/Cat scratch disease)
⑬ 심내막염
⑭ 요로 감염
⑮ 그 외
원인 불명의 열의 처치
- 열이 나면서 많이 아프면 병원에 입원한 후 반복 검진을 해서 진단한다.
- 때로는 적절한 임상 검사도 여러 번 반복해야 한다.
- 때로는, 부모가 아이의 체온을 잘못 재거나, 잰 체온을 잘못 읽거나, 잘못된 체온계로 열을 잴 때 실제로는 열이 나지 않는 데도 열이 난다고 호소할 수 있다. 실제로 열이 나지 않는데 아이에게 열이 난다고 해서 원인 불명 열로 오진할 수 있다.
- 하루 종일 난 열의 형태, 또는 그 동안 1~2주 동안 난 열의 형태는 열을 나게 하는 병을 진단하는데 도움이 된다. 그래서 부모가 집에서 열을 재고 기록해야 한다.
- 열이 오랫동안 나는 것 같으면 진짜로 열이 나는지 우선 확실히 체온을 재고 있나 알아보아야 한다.
- 병원에 입원을 한 후, 과거 현재 병력 등을 더 자세히 알아보고, 부모 아닌 간호사 등이 체온을 직접 재어보고 여러 번 반복 진찰을 더 자세히 해 원인 불명 열을 진단할 수 있다.
- CBC 피 검사, 적혈구 침강속도(ESR)검사, 항핵항체(ANA), C-반응성 단백,
- 항스트랩톨리신 O치 검사(ASO 치/스트렙토리신), 소변 화학검사 및 소변 세균배양검사, 간 기능검사, 가슴 X-선 사진, 그 외 다른 종류의 혈액검사, 피, 뇌척수액, 소변, 대변 등으로 세균배양검사, 결핵이 있나 알아보기 위해 투베르쿨린 피부 반응 검사 등을 해 신체의 어느 부위에 어떤 결핵 감염병이나 감염병 이외 다른 병으로 인해 열이 나는지 진단할 수 있다.
- 때로는 이런 임상 검사들 중 어떤 임상 검사는 여러 번 반복 검사하기도 한다.
- 류마티스 열이나 연소성 류마토이드 관절염이 의심되면
- 적혈구 침강속도(Erythrocyte sed rate/ESR) 검사,
- 항핵항체(Antinuclear Antibody/ANA) 검사,
- C-반응성 단백(C reactive protein),
- 항스트랲톨리신 O 치(Antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer) 등을 검사 해보고
- 연소성 류마토이드 관절염을 진단하는데 항핵항체 검사와 류마토이드 인자 검사 등이 진단가치가 있고 전신성 홍반성 낭창을 진단하는데 항핵항체 검사가 유용하다.
- 이와 같이 원인 불명 열을 진단하는 데는 정말로 소아과학을 많이 알아야 한다.
- 원인 불명의 열을 적절히 잘 다루면 좋은 의사로 평가받을 수 있을 정도로 원인 불명 열은 도전적인 임상 건강 문제 중 하나이다.
- 일반적으로 원인 불명의 열을 나게 하는 병을 확실히 진단해 낼 때까지 아스피린, 아세트아미노펜제(Acetaminophen 상품명으로 타이레놀(tylenol) 또는 “아이부프로펜(Ibuprofen) 등의 해열 진통제나 항 염증제로 대증 치료를 될 수 있는 한 하지 않는다.
- 원인 불명 열이 있을 때 소변 화학검사와 소변 세균배양검사의 결과가 비정상으로 나오면 신장 요관 방광 초음파 검사 등으로 후부 요도 밸브 폐쇄증이 있는지 방광 요관 역류가 있는지, 신장 질환 및 요로 감염이 있는지에 따라 알아본다.
- 충수염, 복막염, 복강 내 농양이 의심되면 복강 내 CT 스캔 검사를 할 수 있다.
- 가와사키 병으로 생긴 혈관염 등으로 열이 날 수 있다. 그 때는 그 병을 진단할 수 있는 적절한 검사를 해서 진단한다.
- CBC 피 검사가 비정상이고 열이 계속 나거나 백혈병이 의심되면 골수 천자 검사와 골수 세균 배양 검사를 할 수 있다.
- 그 외 진균 흉곽강 내 림프절염, 폐렴, 사르코이드증, 히스토플라마증 등의 희귀한 병으로 원인 불명 열이 날 수 있다. 그런 병을 의심해 보고 그런 병을 진단하는 데 적절한 검사를 해서 진단할 수 있다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호 백과]- 7권 소아청소년 감염병-원인 불명 열 참조

사진 38. 필요에 따라 소변 화학검사도하고 소변세균배양 검사도 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
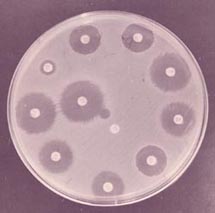
그림 39. 필요에 따라 소변, 피, 대변, 뇌척수액 등으로 세균 배양검사도 한다. 때로는 반복 검사한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
|
다음은 “원인 불명 열, 열만 나요“에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 원인 불명 열
Q.
그밖에
47개월 된 남자 아이입니다. 열흘 전(6월10일)부터 열이 납니다. 해열제를 먹이다 16일 근처
소아과에 갔는데 불명열은 종합병원 진료 권유.
종합병원 뇌수막염 의심. 확인. 아님. 입원. (피검사. 소변검사. x-ray) 별 이상 없음. 입원 중 눈 충혈 눈꼽 끼고 심해져 안약처방. 입술 붉어짐. 39도를 오르락 거리고 해열제 먹여도 38도 이하로 떨어지지 않던 열이 열흘 만에 19일 새벽 36.5도가 됨 19일 오전 퇴원. 여기까지면 얼마나 좋을까요. 다시 열이 나네요.
눈 충혈 여전 하고요. 입술도 빨갛고 마르고. 나아질까요. 불안 지옥이네요. 선생님 말씀이
고프네요.
A.
미니맘
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다. 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
이미 [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제 7권 소아청소년 감염병–원인 불명의 열 (Fever of unknown origin/FUO)을 읽어 보셨으리라 믿습니다.
47개월 된 아이에게 원인 불명의 열이 나면 피, 소변, 대변, 인두, 눈, 뇌척수액 등에서 피검물을 얻어 그로 그람 염색 세균 검사, 세균 배양검사를 적어도 한번, 필요에 따라 여러 번 반복 해보고 필요한 다른 종류의 임상 검사도 해보고 항핵항체(ANA) 검사, 적혈구 침강속도(ESR) 검사, 결핵 피부 반응검사, 류마토이드 인자(Rheumatoid factor), 항스트렙톨리신 O 치(ASO titer), 가슴 X-선 사진, 소변 화학검사, 혈액 화학검사, 심전도 검사 등 여러 가지 임상 검사를 한번 내지, 필요에 따라 여러 번 반복해서 바이러스성 감염병, 부루셀라 병, 장질부사, 야토병(Tularemia/Pahvant Valley plague/ rabbit fever/deer fly fever), 충수염과 그로 인한 농양, 골수염, 연소성 류마티스양 관절염, 염증성 장염, 악성 종양, 완전히 치료되지 않은 뇌막염, 가와사키 병, 묘조병(묘소병), 심내막염, 요로 감염 등을 감별 진단하는 것이 보통입니다.
종합 병원에서 이런 검사를 이미 다 했을 줄 압니다.
주신 정보를 토대로 진단한다면 혹시 가와사키병([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제 7권 소아청소년 감염병 참조)인가 의심해 봅니다.
아직 문제가 있으면 소아 청소년과에서 진찰 진단을 받으시고 이 문제에 관해서 상담
하시기 바랍니다. 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
|
다음은 “원인 불명 열, 아이 열의 원인은? “에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 원인 불명의 열
Q.
정말 심난한 맘으로 글을 올립니다.
96년 11월생 딸 하나를 키우는 엄마입니다. 아이가 모유를 전혀 못 먹고 자란 탓인지 태어나서 지금껏 거의 매달 열감기로 고생하고 있습니다. 동네 소아과 의사 선생님께선 별 이상 없다시며 종합병원 검진을 권하지 않으시구 해서 저두 큰 병은 아니려니 하는 생각에 그냥 처방대로 따르긴 하는데.. 아이가 아플 땐 열이 아주 높습니다. 평균 5일 정도 아프구요. 부르펜 시럽으로 열을 떨어뜨리는 시간도 얼마 못가구. 괜찮다고 하시지만 정말 괜찮은건지!
참고로 평소엔 너무 잘 놀구 밥을 잘 안 먹어서인지 16kg 정도 몸무게가 나갑니다.
편도가 원인인 것 같은데… 열 날 땐 항상 목이 아프다고 하거든요. 한의원에서 약도 몇 번을 먹었어요. 물론 몸에 열이 많은 거라며 걱정 말라긴 하지만 6살인데 이렇게 매달 열감기로 고생 하는 게 크게 걱정할 일이 아닌가요? 편도 수술 문제도 고려하고 있습니다.
꼭 답변을 부탁드리면서…
A.
연아님
안녕하세요. 좋은 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 컴퓨터 문제로 답변이 늦어 죄송합니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등을 자세히 그리고 더 많이 알면 답변을 드리는데 도움이 많이 됩니다.
주신 정보를 토대로 답변을 드리겠습니다.
신체 어느 한 국소나 신체 전부(전신)에 전신성 바이러스성 감염, 박테리아성 감염, 또는 그 외 다른 병원체 감염으로 인해서 전신성 감염병이 생길 때, 백혈병이나 암, 류마티스 열, 류마티스관절염, 가와사키 병, 요로감염, 또는 약물 부작용 등으로 열이 날 수 있습니다.
그 중 열을 나게 하는 가장 흔한 원인은 전신성 바이러스 감염병이나 박테리아 감염병입니다.
어떤 병원체 감염에 의해서 신체 어느 국소에 감염병이 생겼는지 알아보고 그 원인에 따라서 적절히 치료해야 합니다.
따님의 경우는 인두염과 편도염(인두 편도염)으로 열이 났던 것으로 압니다.
인두 편도염을 일으키는 원인 병원체 중 가장 흔한 병원체는 바이러스이고 그 다음은 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균입니다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제 8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환 참고.
바이러스성 인두 편도염을 앓을 때의 증상 징후는 감기를 앓을 때의 증상 징후와 비슷한 때가 많습니다.
A군 베타 용혈성 연구균성 인두 편도염을 앓을 때는 인두가 몹시 아프고 열이 나는 것이 보통입니다. 적절한 항생제로 치료 하지 않으면 그런 증상이 계속 되고 계속 더 아픈 것이 특징입니다.
3세 이전 아이들에게는 A군 베타 용혈성 연구균성 인두 편도염은 잘 생기지 않는 것이 보통입니다.
바이러스성 인두 편도염과 A군 베타 용혈성 연구균성 인두 편도염의 감별 진단을 해야 합니다. 증상 징후과 진찰 소견을 참고해서 감별 진단을 할 수 있지만 인두와 편도의 피검물 점액을 채취해서 A군 베타 용혈성 연구균 항원 항체 응집검사를 하든지 A군 베타 용혈성 연구균 세균배양검사(스트렙토 테스트)를 해서 감별 진단을 합니다. 그 검사 결과가 양성이면 A군 베타 용혈성 연구균 인두 편도염에 걸렸다고 진단할 수 있습니다.
다음에 환아의 목 안이 아프면서 열이 나면 A군 베타 용혈성 연구균 균배양 검사(스트렙토 테스트)검사 등을 꼭 해서 연구균성 인두 편도염을 확진해 보십시오.
또 자녀들이 목안이 아프다고 하면 부모가 전등불로 목 안을 비춰보면 편도와 인두가 붓고 빨간 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 자녀가 인두 편도염을 앓는다고 의심하면 의사의 진단 치료를 받으러 소아청소년과로 오는 것이 미국 부모들이 하는 자녀 양육 방법입니다.
평소에도 부모가 목안을 들여다보는 연습을 하십시오.
그래서 부모들도 자녀의 입안 구조에서 어떤 것이 정상인지 비정상인지를 평소에 알아두는 것도 좋을 것입니다.
승용차에 가스도 넣을 줄 모르고 차바퀴가 펑크 나도 타이어를 갈아 줄 모르고 오일을 바꿀 줄도 모르면 곤란하지요.
편도 농양이라는 병이 있는데 이 편도 농양을 한번 앓은 후에는 이 병이 재발되는 경향이 있습니다.
일반적으로 이 병을 앓으면 편도 적제 수술치료를 받는 것이 보통입니다. 자녀가 혹시 편도 농양을 앓고 있는지도 의심해 봅니다.
아프지 않은 평소 어느 때 소변검사를 꼭 하시고 또 열이 나면서 아플 때 확실한 진단 없이 항생제를 쓰기 전에 소변검사를 꼭 하시면 좋을 것 같습니다.
소아 요로 감염병으로 자녀의 겨우 같이 열이 날 수 있습니다.
더 자세한 것은 아이가 아프지 않을 때도 소아청소년과에 가셔서 아이의 의사 선생님의 검진을 받고 이 문제에 관해 상담하시는 것이 좋을 것 같습니다. 열.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아청소년 감염병–원인 불명의 열.
제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환–감기, 인두 편도염.
제 10권 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기계 질환–요로 감염 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
소아과에서 진찰 진단 치료를 받고 상담하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주세요. 감사합니다.
이상원 드림
|
다음은 “원인 불명의 열, 열이 너무 오래납니다.”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 원인 불명의 열, 열이 너무 오래납니다.
Q.
안녕하세요.
저희 아가는 11개월 접어든 아가입니다.
7월 6일날 저녁부터 열나고 다음날은 토하고 설사를 해서 다니던 동네소아과를 갔더니 장염에 급성위염에 목도 부었다고 해서 탈수될까봐 링겔도 맞았습니다.
그러다가 토하는 것도 좋아지고 변도 닥터호프를 먹이면서 약을 계속 먹였더니 지금은 많이 좋아져있습니다. 그런데 열이 계속 나고 있습니다.
7월 11일 수요일까지 동네 병원에 다니다가 동네병원에서 소견서를 써주며 열이 너무 오래 가니깐 종합병원급에 가서 검사를 받아보라고 해서 혈액검사 소변검사까지 다 했는데 별 이상이 없다고 하네요..
종합병원에 옮기면서 계속 링겔(항생제를 섞었다네요)맞고 어제 일요일날 아침에 한번 저녁에 한번 38도 조금 넘는 열이 또 났어요. 미열(37도1~3)은 두 번 정도 나구요. 그리고 오늘은 지금까지 미열이 3번 났어요.
오늘도 큰 병원에 다녀왔어요. 어제부터는 링겔을 맞지 않아요. 뾰족히 무슨 병인지도 가르쳐주지 않고, 목이 부었다가 요즘 유행하는 뇌막염으로 재발하지 않았나 하시더라구요..
근데 엄마 입장으로서 열이 10일 이상 너무 오래 나서 걱정이 되네요. 다른 분들이 다른 큰병원 가서 다시 검사를 한번 더 해보라고 하던데…
어떡하면 좋을까요… 너무 걱정됩니다. 답변 부탁드릴께요…
A.
손아님
안녕하십니까. 좋은 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 걱정이 많이 되시겠습니다.
이제 열이 거의 나지 않으니까 별로 걱정하시지 않아도 될 것 같습니다.
그러나 말씀하신 대로 어떤 병을 치료하고 계신지 저도 가늠할 수 없습니다.
열이 일주일 이상 계속되고 열나는 원인을 확실히 모를 때는 원인 불명 열(Fever of unknown origin)이란 병명을 붙일 수 있습니다.
요즘 의학이 많이 발달되어 열을 나게 하는 원인되는 병을 전보다 아주 쉽게 찾아서 원인 불명의 열이라고 진단 붙이는 경우가 아주 드뭅니다. 그래서 전에 원인 불명 열의 정의도 다시 정리해야 할 것 같습니다.
그러나 요즘도 전염성 단핵구증 등 바이러스성 감염병으로 열이 10일 이상 나는 경우도 있습니다. 이 병으로 열이 나는 것 같지는 않습니다.
열이 나지 않고 잘 먹고 잘 놀면 아무 임상 검사도 할 필요 없고 치료도 할 것 없이 2~3일 동안 더 관찰적 치료를 하면서 항문체온을 재보시지요.
계속 열이 나지 않고 잘 놀면 걱정하실 필요도 없을 것 같습니다.
만일 원인을 모르면서 열이 계속 나면 다음과 같은 임상 검사들 중 일부 또는 전부를 해서 다음 열거한 병들을 감별 진단하면 좋을 것입니다.
뇌척수액 그람 염색 현미경 세균 검사 및 곰팡이 검사, 바이러스, 박테리아 든 뇌척추액 세균배양검사, 뇌척수액 단백질 농도와 당 농도, 혈구계산 검사, 뇌척수액 소변 그람 염색 현미경 검사, 소변 화학 검사 및 소변 세균배양 검사, 혈액 균배양 검사, 인두 점막 균배양 검사, 대변 균배양 검사, 적혈구 침강속도 검사, 결핵균 피부 반응 검사, 간 기능 검사, CBC 피 검사. 가슴 X-선 사진 검사, 류마토이드 인자 검사(류머토이드 인자), 항핵항체검사 등을 해 뇌막염, 중이염, 축농증, 편도염, 폐렴, 결핵, 위장염, 요로 감염, 류마티스 관절염, 류마토이드 관절염, 불완전 치료 뇌막염 등을 감별 진단해야 합니다.
아기의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등을 종합해서 병을 진단 치료하는 것이 이상적이지만 주신 정보를 참작해서 답변을 드렸으니 참고하시기 바랍니다.
소아청소년과에서 추적 진찰 진단 치료를 받고 상담하시기 바랍니다.
열, 원인 불명의 열 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
그리고 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Fever of unknown origin (FUO)
Definition of unexplained fever

Photo 8-6. Take your temperature to see if you have a fever.
- Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
- A fever of unknown cause is known as fever when the fever continues to occur in children for 8 days or longer, and in adults for 3 weeks or longer, but the obvious cause of the fever is not found by examination findings and the first clinical examination.
- It is also defined as an unknown fever or an unknown fever),
- A fever of at least 38.3°C (101°F) or higher in 14 days lasting for at least 4 hours, and at least 4 or more times of that fever is sometimes defined as an unexplained fever.
- sauce; Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.245
- It is also defined differently.
Causes of unexplained fever
- Fever is diagnosed as unexplained fever when a fever continues for 3 weeks or more in adults and 8 days or more in children, but the cause of fever is not found even after diligently searching for the cause.
- Fever when the cause of the fever is found in the hospital for 7 days and the cause is not found is sometimes diagnosed as a fever of unknown cause.
- When It looks for the cause of the fever for more than 3 weeks outside the hospital, it is called an unknown fever when I cannot find the cause of the fever.

Figure 37. If the fever persists for 8 days or more (for children), or continues for 3 weeks or longer (for adults) without being able to clearly determine the cause of the fever from the first examination findings and clinical examination.
- In this case, it can be defined as a fever of unknown cause.
- Vol. 21 Children and Adolescents Home ∙ School Nursing References and Sources-11.
Diagnosis of fever of unknown origin
If the fever continues for 8 to 2 weeks, and the cause of the fever is not clearly found even after the past medical history, family history, current medical history, symptoms, signs, examination findings, etc.
- are synthesized and appropriate clinical tests are performed, it is called an unknown fever.
- These unexplained columns are defined in several ways.
- Tuberculosis, other infectious diseases, cancer, leukemia, A fever can be caused by a urinary tract infection.
- Even if you repeat appropriate examinations and clinical tests to find out why you have a fever when you have such a disease, you may not be able to make a diagnosis for the first time.
- Infected with Salmonella from pet turtles or snakes and contracted Salmonella infectious disease,
- After eating poorly managed melon or watermelon,
- you can become infected with Salmonella and get a Salmonella infectious disease.
- When suffering from these infectious diseases,
- the diagnosis may not be made for the first few days, and the diagnosis may be made with unexplained fever.
- Malaria, which is only prevalent in that region when traveling to a certain region or country,
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
Q
- You can get a fever for more than 8 days due to a specific infectious disease in a specific area, such as fever.
- Some people are diagnosed with unexplained fever because they do not know whether they have such a disease and have not been able to make a diagnosis for the first time.
- After eating raw milk, you can get Brucellosis disease and have a fever for more than 8 days.
- After eating uncooked food, you can get infectious diseases such as larval organ transfer syndrome and intestinal sputum,
- and you may continue to have a fever for more than 8 days.
- Twenty percent of unexplained fevers can go away spontaneously without knowing the cause of the fever, even if you try to find the cause of the fever.
80% of unexplained fevers in children and adolescents are caused by infectious diseases or diseases such as:
① Viral (sex) infectious disease
② Brucella disease
③ Jangjil adverb
④ Tularemia
⑤ Appendicitis and resulting abscess
⑥ osteomyelitis
⑦ Combustion rheumatoid arthritis
⑧ Inflammatory enteritis
⑨ malignant tumor
⑩ Meningitis that is not completely cured
⑪ Kawasaki disease
⑫ Cat scratch disease
⑬ endocarditis
⑭ urinary tract infection
⑮ Other
Treatment of unexplained fever
- If you have a fever and get sick a lot, you should be admitted to the hospital and have repeated checkups to diagnose.
- Sometimes the appropriate clinical tests also need to be repeated several times.
- Sometimes, parents may complain that their child has a fever even though they don’t actually get a fever when they take the child’s temperature incorrectly, read the temperature incorrectly, or take a fever with the wrong thermometer.
- If their child doesn’t actually have a fever, but your child has a fever, you can misdiagnose it as a fever of unknown cause.
- The type of fever you have all day, or for a week or two during that time, is helpful in diagnosing the disease that causes the fever.
- That’s why parents need to measure and record the heat at home.
- If you feel like your child has a fever for a long time, you should check your child’s temperature first to see if your child really had a fever.
- After being admitted to the hospital, you can find out more about your child past and present medical history, measure your child’s body temperature directly by a nurse, etc., and repeat medical examinations several times to diagnose an unexplained fever.
- CBC blood test, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test, antinuclear antibody (ANA), C-reactive protein, Anti-streptolysin O level test (ASO level/Streptolysin), urine chemistry test and urine bacterial culture test, liver function test, chest X-ray, other types of a blood test, blood, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, feces, etc.
- By doing a bacterial culture test and a tuberculin skin reaction test to find out if there is tuberculosis, you can diagnose which tuberculosis infectious disease or other diseases other than the infectious disease cause fever in any part of the body.
- Sometimes some of these clinical tests are repeated several times.
- If you suspect rheumatoid fever or juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, Erythrocyte sed rate/ESR test, Antinuclear Antibody/ANA test, C-reactive protein, Test for antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer, etc.
- Antinuclear antibody tests and rheumatoid factor tests are valuable for diagnosing juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, and antinuclear antibody tests are useful for diagnosing systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Diagnosing unexplained fever like this really requires a lot of pediatric science.
- Unexplained fever is one of the challenging clinical health problems, so it can be evaluated by a good doctor if properly handled.
- In general, symptoms can be treated with antipyretic analgesics or anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol under the trade name Acetaminophen), or “Ibuprofen” until the disease-causing fever of unknown cause is clearly diagnosed.
- As long as you don’t.
- If the result of the urine chemistry test and urine bacterial culture test is abnormal when there is a fever of unknown cause, use a renal ureter, bladder ultrasound, etc. to determine whether there is posterior urethral valve obstruction, bladder ureter reflux, kidney disease, or urinary tract infection.
- If appendicitis, peritonitis, or abscess in the abdominal cavity are suspected, an intraperitoneal CT scan can be done.
- You may get fever due to vasculitis caused by Kawasaki disease.
- In that case, it is diagnosed by performing an appropriate test to diagnose the disease.
- If the CBC blood test is abnormal and you have a fever or leukemia is suspected, a bone marrow puncture test and a bone marrow bacterial culture test may be done.
- Other rare diseases such as fungal intrathoracic lymphadenitis, pneumonia, sarcoidosis, and histoplasmosis may cause unexplained fever.
- It can be diagnosed by suspicion of such a disease and by performing appropriate tests to diagnose it.
- www.drleepediatrics.com-Vol. 7 Pediatric Infectious Diseases-See column of unknown cause

Photo 38. If necessary, a urine chemistry test and a urine bacterial culture test are also performed. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- bacterial_culture_and_sensitivity_test-2s.jpg

Figure 39. Bacterial culture tests are also performed with urine, blood, feces, cerebrospinal fluid, etc. as needed. Sometimes repeated tests.
- Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
The following is an example of a Q&A on health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet regarding “fever of unknown cause, do you have a fever”.
Q&A. fever of unknown cause
Q. etc He is a 47-month-old boy. I have fever since ten days ago (June 10). Around 16 days after taking antipyretics, I went to the pediatrician, but for an unknown fever, I was recommended to go to a general hospital. General hospital suspected of meningitis. Confirm. no. Admission. (Blood test, urine test, x-ray) No abnormality. During the hospitalization, redness in the eyes got worse, and eye drops were prescribed. redness of the lips.
The fever that went up and down 39 degrees and did not drop below 38 degrees even after taking antipyretics became 36.5 degrees in the morning of the 19th in 10 days. I was discharged on the morning of the 19th. How good would it be to get here? I have a fever again. My eyes are still bleeding. Lips are also red and dry. will it get better It’s anxiety hell. teacher’s words I’m sick. A. mini mom Hello. Thanks for asking. That’s a good question.
The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family history, examination findings, and clinical tests, the more helpful it is to give you an answer. We will give you an answer based on the information you provided. I believe you have already read [Parents should also become at least the half-doctors – Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing] – Volume 7 Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents – Fever of unknown origin/FUO. If a 47-month-old child has a fever of unknown cause, obtain specimens from blood, urine, feces, pharynx, eye, cerebrospinal fluid, etc. Antinuclear antibody (ANA) test, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test, tuberculosis skin reaction test, rheumatoid factor, antistreptolysin O level (ASO titer), chest X-ray, urine Multiple clinical tests, such as chemical tests, blood chemistry tests, and electrocardiograms, are performed once or repeatedly as needed. fever), appendicitis and its abscesses, osteomyelitis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory enteritis, malignant tumors, untreated meningitis, Kawasaki disease, Myocarditis, endocarditis, and urinary tract infection are common.
I think the general hospital has already done all these tests. If the diagnosis is based on the information you have provided, I suspect that it is Kawasaki disease ([Parents should also become anti-doctors – Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing – Refer to Volume 7 Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents). If there are still problems, consult a pediatrician and consult about this problem. Please. If you have any more questions, please feel free to contact us again. thank you. Lee Sang-won Dream
Next, “Fever of unknown cause, what is the cause of fever in children?
This is an example of a question-and-answer question for children and adolescents on the Internet about “.
Q&A. fever of unknown cause
Q. I am writing this with a very sad heart. Born in November 1996, I am a mother of one daughter. Perhaps because her child grew up not breastfed, she has been suffering from a cold almost every month since she was born.
She said that the local pediatrician said she was okay and did not recommend a general hospital check-up, so I thought that it was not a serious illness, so I just follow the prescription.. When the child is sick, the fever is very high.
She’s been sick for an average of 5 days. She didn’t even have time to drop the fever with Buffen Syrup. She says she’s okay, but is she really okay? For reference, she usually plays too well and doesn’t eat well, so she weighs about 16kg. I think the tonsils are the cause…
They always say they have a sore throat when they have a fever. She took medicine a few times at the oriental clinic. Of course, don’t worry about the fact that she has a lot of heat in her body. One-way surgery is also being considered. I’m begging you for an answer… A.
Miss Yuna Hello. Thanks for the nice question. Sorry for the late reply due to computer problems. Knowing your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family history, examination findings, and clinical tests in detail, and more will help us to give you an answer. We will respond based on the information you have provided. When a systemic infectious disease is caused by a systemic viral infection, bacterial infection, or other pathogenic infection in any part of the body or the whole body (systemic), leukemia, cancer, rheumatic fever, rheumatoid arthritis, Kawasaki disease, urinary tract infection, Or, you may have a fever due to a side effect of the drug.
Among them, the most common cause of fever is a systemic viral infection or bacterial infection. It is necessary to find out which part of the body caused the infectious disease by which pathogenic infection and treat it appropriately according to the cause. In the case of my daughter, I understand that she had a fever due to pharyngitis and tonsillitis (pharyngeal tonsillitis). Among the pathogens that cause pharyngeal tonsillitis, the most common pathogen is a virus, followed by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.
www.drleepediatrics.com] – Refer to Volume 8 Respiratory Diseases in Children and Adolescents.
Symptoms of viral pharyngotonsillitis are often similar to those of having a cold. When you have group A beta-hemolytic research bacillus pharyngeal tonsillitis, it is normal to have a very sore throat and a fever.
If not treated with appropriate antibiotics, these symptoms persist and are characterized by continued pain. Group A beta-hemolytic labile pharyngeal tonsillitis is not common in children before the age of 3 years. A differential diagnosis should be made between viral pharyngeal tonsillitis and group A beta-hemolytic pharyngeal tonsillitis.
Differential diagnosis can be made by referring to symptom signs and examination findings, but pharyngeal and tonsil specimens are collected and tested for antigen-antibody aggregation of group A beta-hemolytic bacteria, or group A beta-hemolytic bacteria culture test (strepto test). differential diagnosis.
If the test result is positive, it can be diagnosed that you have group A beta-hemolytic pharyngeal tonsillitis. If the child has a sore throat and fever next time, be sure to test for group A beta-hemolytic research bacteria culture (strepto test) to confirm the diagnosis of research bacterial pharyngeal tonsillitis.
Also, if the child complains of a sore throat, the parents can see the tonsils and pharynx swollen and red when the parent shines a light on the inside of the neck. If you suspect that your child has pharyngeal tonsillitis, coming to the Department of Pediatrics for diagnosis and treatment by a doctor is the way parents in the United States are raising their children.
Practice looking into the eyes of your parents on a regular basis. So, it would be good for parents to know what is normal and what is abnormal in the structure of their child’s mouth on a regular basis.
If you don’t know how to put gas in your car, if the wheel is flat, you don’t know how to change tires or change the oil. There is a condition called tonsil abscess, which tends to recur after you have had one. In general, if you have this disease, it is common to receive tonsillectomy surgery.
Also suspect that your child may have a tonsil abscess.
It would be a good idea to have a urine test at any time when you are not sick, and to do a urine test before using antibiotics without a definitive diagnosis when you are sick with a fever. With a childhood urinary tract infection, your child may barely have a fever. For more details, even if the child is not sick, it would be better to go to the pediatric department and have the child’s doctor check-up and discuss this issue. Ten.
www.drleepediatrics.com – Vol. 7 Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents – Fever of unknown cause. Book 8 Respiratory Diseases in Children and Adolescents – Colds and Pharyngeal tonsillitis.
Please refer to Volume 10 Children and Adolescents Kidney and Urogenital Disorders – Urinary Tract Infection, etc. Please consult a pediatrician for diagnosis, diagnosis and treatment. If you have any more questions, please contact us again. thank you. Lee Sang-won.
The following is an example of a Q&A for health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet about “fever of unknown cause, fever lasts too long.”
Q&A. Unexplained fever, fever too long.
Q. Hello. Our baby is 11 months old.
I had a fever from the evening of July 6th, and the next day I had vomiting and diarrhea. Then my vomiting got better and I continued to take medicine while feeding Dr. Hope, and now I feel much better. But the fever continues. I went to the local hospital until Wednesday, July 11th, and the local hospital wrote me a report and the fever went on for a long time, so I went to the general hospital and got a test. As I was transferred to the general hospital, I kept getting Ringel (I mixed antibiotics) and had a fever of a little over 38 degrees, once in the morning and once in the evening on Sunday. I have a mild fever (37 degrees 1-3) about twice. And today, I have had a low fever 3 times so far. I went to a big hospital today.
I haven’t taken Ringel since yesterday. They didn’t even tell me what the disease was, and they said that my neck was swollen and then recurred due to meningitis, which is popular these days. But, as a mother, I am worried because my fever has lasted more than 10 days. Others told me to go to another big hospital and do the test again…
What should I do… I’m so worried. Please answer me… A. not grandson Hello. Thanks for the nice question. You will be very worried. Now that there is almost no fever, I don’t think you need to worry too much.
But as you said, I can’t even guess what kind of disease you are treating. When a fever lasts more than a week and the cause of the fever is unknown, it may be termed Fever of unknown origin. With the development of medicine these days, it is very rare to find a disease that causes fever more easily than before and attach it as a fever of unknown cause.
So it looks like I’ll have to rearrange the definition of unexplained columns before as well. However, even these days, there are cases of fever for more than 10 days due to viral infections such as infectious mononucleosis.
I don’t think I’m having a fever with this disease. If you do not have a fever and eat well and play well, you do not need any clinical tests and you do not need any treatment, continue observational treatment for 2 to 3 days and measure your anal body temperature.
As long as you don’t have a fever and play well, there’s no need to worry. If the fever persists without knowing the cause, some or all of the following clinical tests may be useful to differentially diagnose the diseases listed below.
Cerebrospinal fluid gram stain microscopic examination and fungal test, cerebrospinal fluid culture test containing viruses and bacteria, cerebrospinal fluid protein concentration and sugar concentration, hemocytometry test, cerebrospinal fluid urine gram stain microscopic test, urine chemistry test, and urine bacterial culture test, blood bacteria Culture test, pharyngeal mucosa culture test, stool culture test, erythrocyte sedimentation rate test, Mycobacterium tuberculosis skin reaction test, liver function test, CBC blood test. Chest X-ray examination, rheumatoid factor test (rheumatoid factor), antinuclear antibody test, etc., meningitis, otitis media, sinusitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, gastroenteritis, urinary tract infection, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, incompletely treated meningitis, etc. should be differentially diagnosed.
It is ideal to diagnose and treat the disease by synthesizing the baby’s age, sex, past medical history, family history, examination findings, and clinical tests, but please refer to the answer as we have taken into account the information you have given us. Please consult with the Department of Pediatrics for follow-up, diagnosis and treatment. See Fever, Unexplained Fever, etc. And if you have any more questions, please feel free to contact us again. thank you. Lee Sang-won Dream
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Fever of Unknown Origin February 3, 2022, N Engl J Med 2022; 386:463-477
-
Oral Health The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stuart D.Josell
-
Pediatric Oral Health Stuart Jose
-
Ann L. Griffen, DDS, MS
-
Atlas Pediatric Physical Diagnosis Frank A Oski
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Gray’s Anatomy
-
제19권 소아청소년 안과 질환 참조문헌 및 출처
- Habilitation of The handicapped Child, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Robert H Haslam, MD.,
-
Pediatric Ophthalmology, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Leonard B. Nelson, M.D.
-
Pediatric Ophthalmology, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Lois J. Martyn, M.D.
-
Pediatric Ophthalmology, Edited by Robison D. Harley, M.D.
-
The Pediatric Clinics of North America, David Tunkel, MD., Kenneth MD Grundfast, MD
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.